Describe the Process of Carbon Cycle
Since our planet and its atmosphere form a closed environment the amount of carbon in this system does not change. Both physical and biological processes in the ocean affect the carbon cycle.
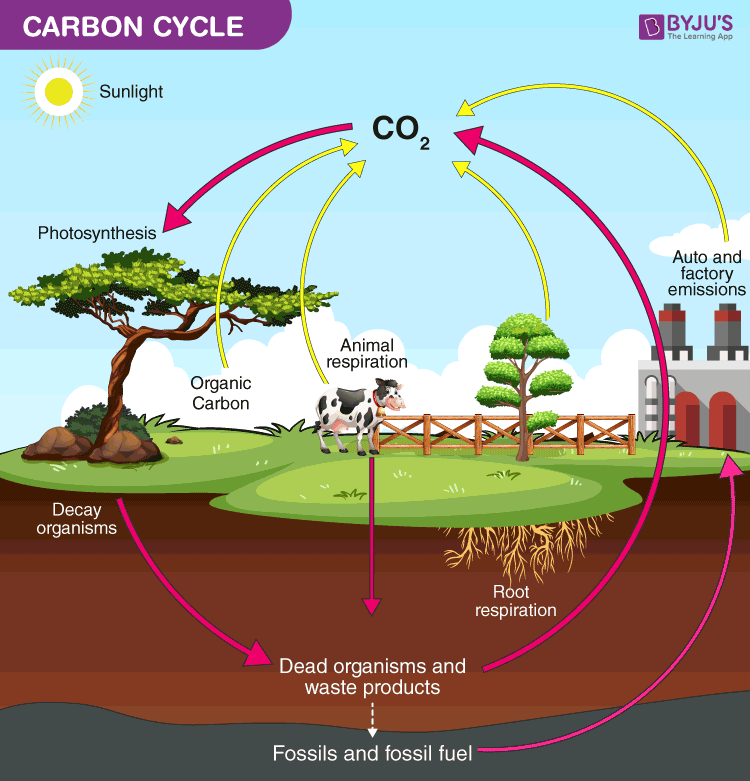
Carbon Cycle Definition Process Diagram Of Carbon Cycle
Carbon is used by plants to build leaves and stems which are then digested by animals and used for cellular growth.

. Carbon present in the atmosphere is absorbed by plants for photosynthesis. Following are the main steps that are involved in the process of the carbon cycle. The carbon cycle is easiest to understand in terms of its processes and how carbon is converted.
As written this lesson is designed to fully meet this standard. CO 2 H 2 Olight energyCH 2 OO 2. In a process called photosynthesis.
The same carbon atoms that exist in your body today have been used in many other molecules since time began - in a tree in a plant and even in. Since carbon exchanges with the biosphere biological processes need to be considered in climate science. Along with the nitrogen cycle and the water cycle the carbon cycle comprises a sequence of events that are key to make Earth capable of sustaining life.
As an animal breathes respires it exhales carbon dioxide returning it back to the atmosphere. Due to the importance of CO 2 as a greenhouse gas the carbon cycle is a crucial part of the climate system. The movement of carbon from reservoir to reservoir is known as the carbon cycle.
Up to 24 cash back The Carbon Cycle Step 1 Carbon enters the atmosphere as carbon dioxide from respiration breathing and combustion burning. When an animal or plant dies it is broken down by bacteria and fungi and again the carbon is released this process is called decomposition. Photosynthesis plants absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and form it into sugar starch and other organic.
The carbon cycle is the biogeochemical cycle by which carbon is exchanged among the biosphere pedosphere geosphere hydro -. The slow carbon cycle involves five key stages in the movement of carbon around the cycle that takes place over many tens and hundreds of millions of years. Oxygen is a by-product of this reaction which is summarized as.
These four main reservoirs of carbon are interconnected by pathways of exchange. Algae and terrestrial green plants producers are the chief agents of carbon dioxide fixation through. They use energy from the sun to chemically combine carbon dioxide with hydrogen and oxygen from water to create sugar molecules.
The three key processes and the conversions are shown in the table below. Carbon cycle in biology circulation of carbon in various forms through nature. The Carbon Cycle Step 3.
Animals that eat plants digest the sugar molecules to get energy for their bodies. Where the carbon is located in the atmosphere or on Earth is constantly in flux. Processes involved in the carbon cycle are.
Noun the cycle of carbon in the earths ecosystems in which carbon dioxide is fixed by photosynthetic organisms to form organic nutrients and is ultimately restored to the inorganic state as by respiration protoplasmic decay or combustion. The carbon cycle describes the process in which carbon atoms continually travel from the atmosphere to the Earth and then back into the atmosphere. Plants to make carbohydrates in photosynthesis.
It describes the movement of carbon as it is recycled and reused throughout the biosphere as well as long-term processes of carbon sequestration to and release from carbon sinks. The carbon cycle is part of the broader biogeochemical cycles which include. Respiration excretion and decomposition release the carbon back into the atmosphere or soil continuing the cycle.
This then interacts with. The basic idea is that plants capture light energy and use it to split water molecules and then combine the products with carbon dioxide to make carbohydrates which are used for fuel and construction of the plant. Almost all of these autotrophs are photosynthesizers such as plants or algae.
Carbon can be stored in a variety of reservoirs including plants and animals which is why they are considered carbon life forms. The Carbon Cycle moves in two major ways known as the fast cycle and slow cycle. Carbon is a constituent of all organic compounds many of which are essential to life on Earth.
Direct CO 2 absorption as part of the atmosphere-ocean exchange is supplemented by the erosion of carbon-rich terrestrial. Carbon is returned to an inorganic state in a number of ways. Carbon moves from the atmosphere to the land ocean and life through biological chemical geological and physical processes in a cycle called the carbon cycle.
Autotrophs capture carbon dioxide from the air or bicarbonate ions from the water and use them to make organic compounds such as glucose. The biological carbon cycle Carbon enters all food webs both terrestrial and aquatic through autotrophs or self-feeders. The carbon cycle is a complex cyclical process through which all of the carbon atoms in existence rotate.
Physical oceanography influences the carbon cycle through its modulation of the biology and also through processes that control carbonate chemistry temperature alkalinitysalinity and carbon dioxide flux rates between the air-sea interface surface wind speeds. The Carbon Cycle Step 2 Carbon dioxide is absorbed by producers life forms that make their own food eg. Carbon Introduction to Climate Science.
The biologicalphysical carbon cycle can be described as the process by which carbon is exchanged between the four main carbon reservoirs the atmosphere biosphere hydrosphere and geosphere. These plants are then consumed by animals and carbon gets bio accumulated into their bodies. These producers then put off oxygen.
Feeding moves carbon in the form of biological molecules along the food chain. Photosynthesis consumption respiration and decomposition are the major processes through which carbon moves within the carbon cycle. Describe how these properties of carbon dioxide relate to the carbon cycle.
The carbon is pulled from the air via stoma on a plants leaves. Carbon cycles through the atmosphere biosphere geosphere and hydrosphere via processes that include photosynthesis fire the burning of fossil fuels weathering and volcanism. The transfer of carbon into the oceans from the atmosphere and land surface.
Because some carbon gases are greenhouse gases changes in the carbon cycle that put more carbon in the atmosphere also warm Earths climate. The source of the carbon found in living matter is carbon dioxide CO 2 in the air or dissolved in water.
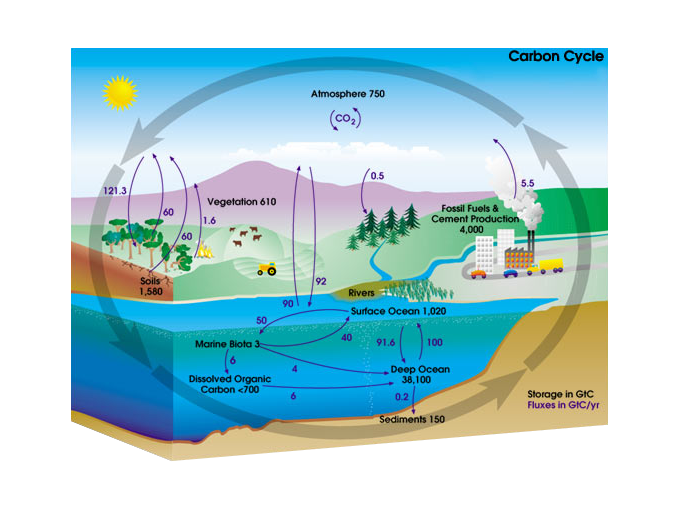
What Is The Carbon Cycle Photosynthesis Decomposition Respiration And Combustion Earth How
The Carbon Cycle Definition Significance Steps And Land Oceanic Cycle
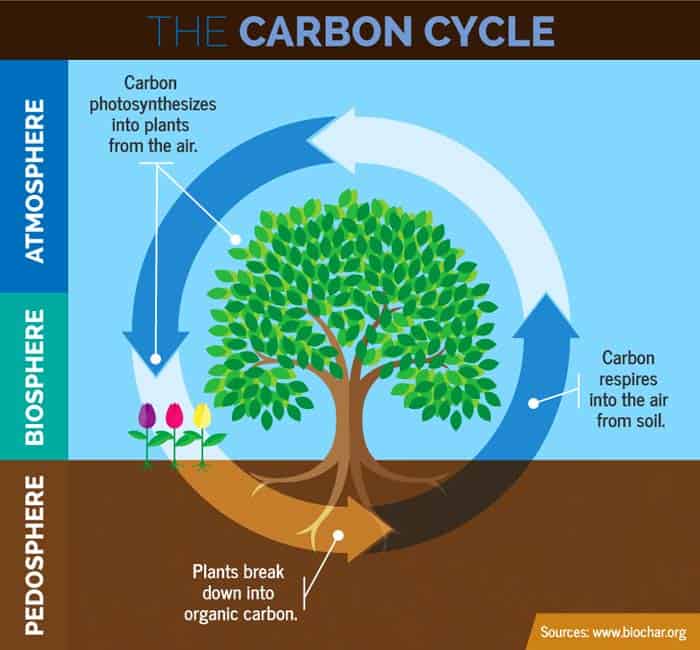
Carbon Cycle Steps Definition Types Importance Biology Explorer

No comments for "Describe the Process of Carbon Cycle"
Post a Comment